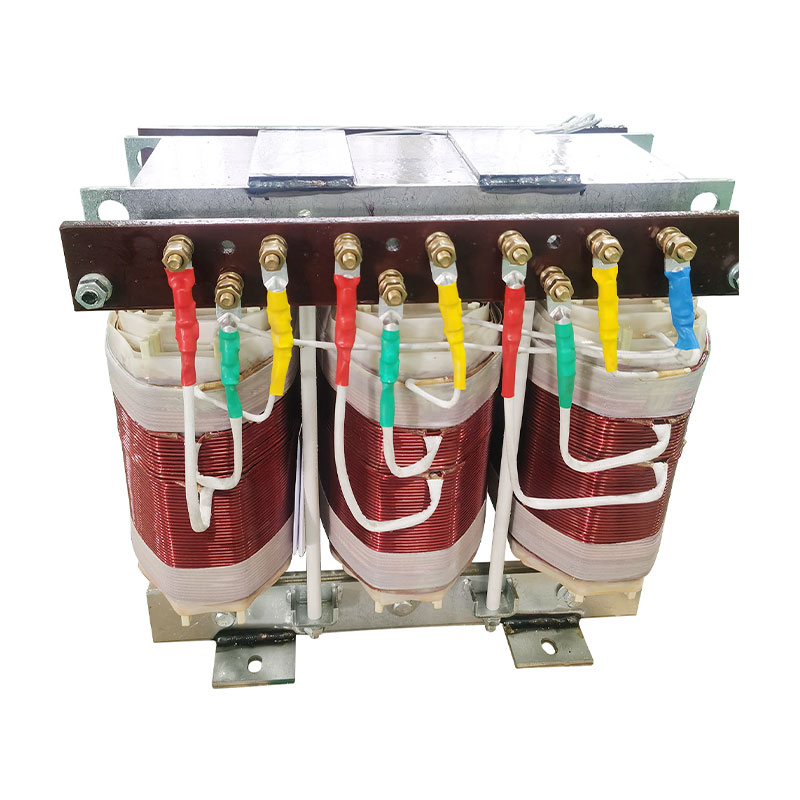
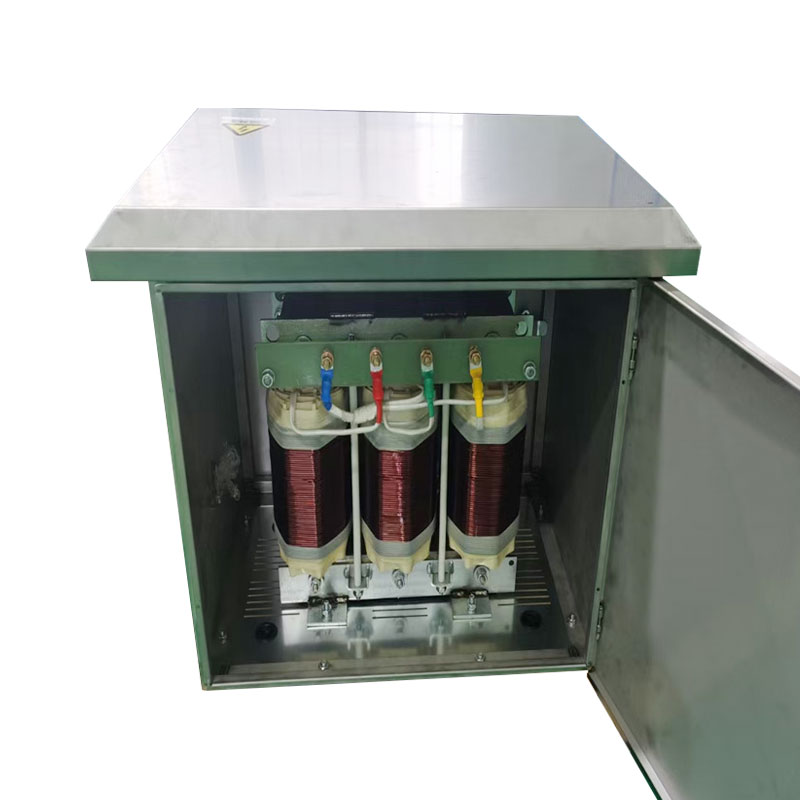
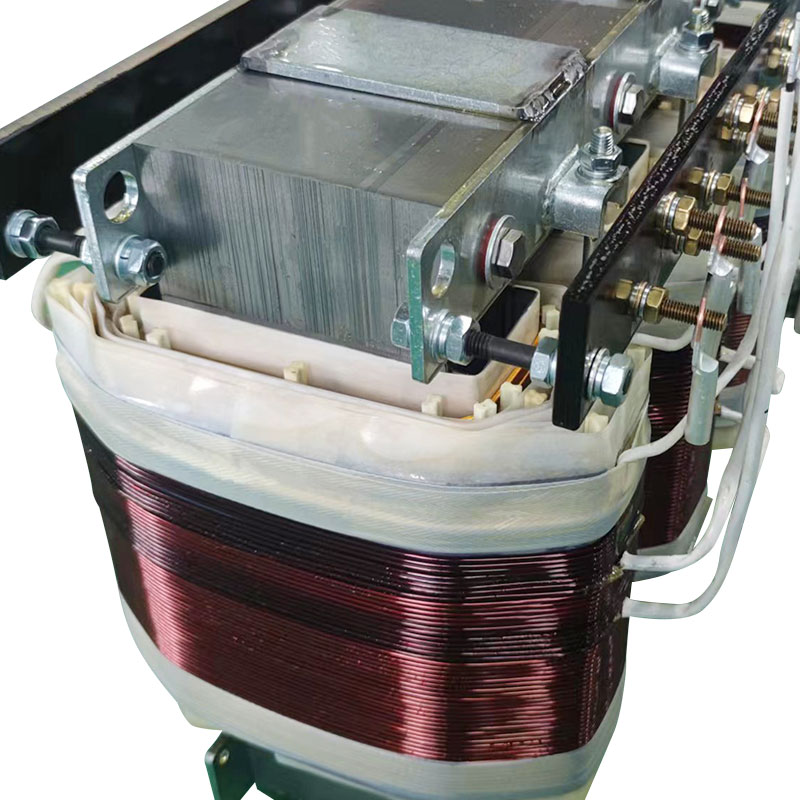
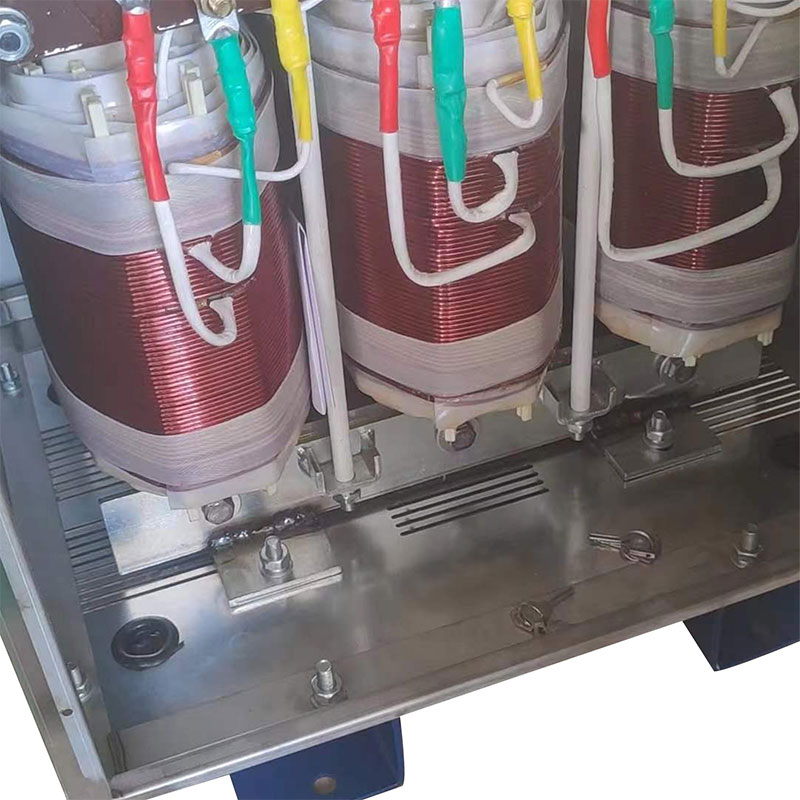
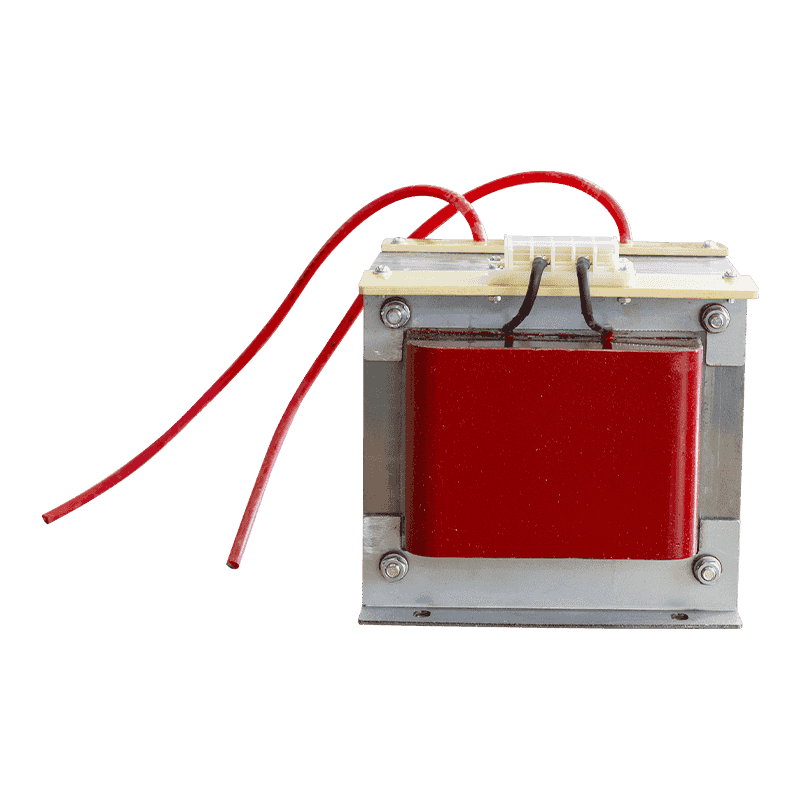
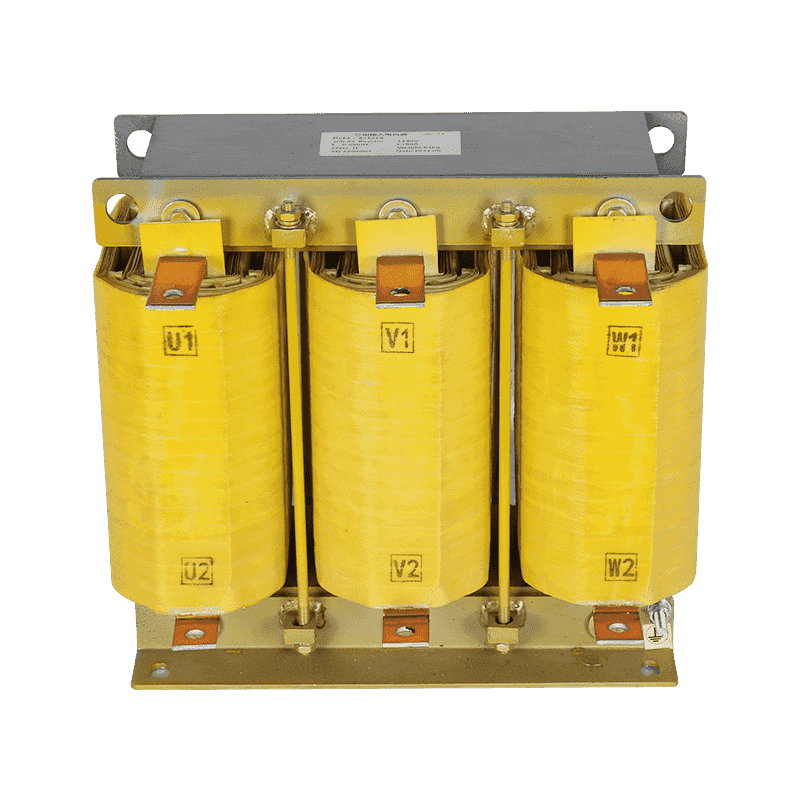
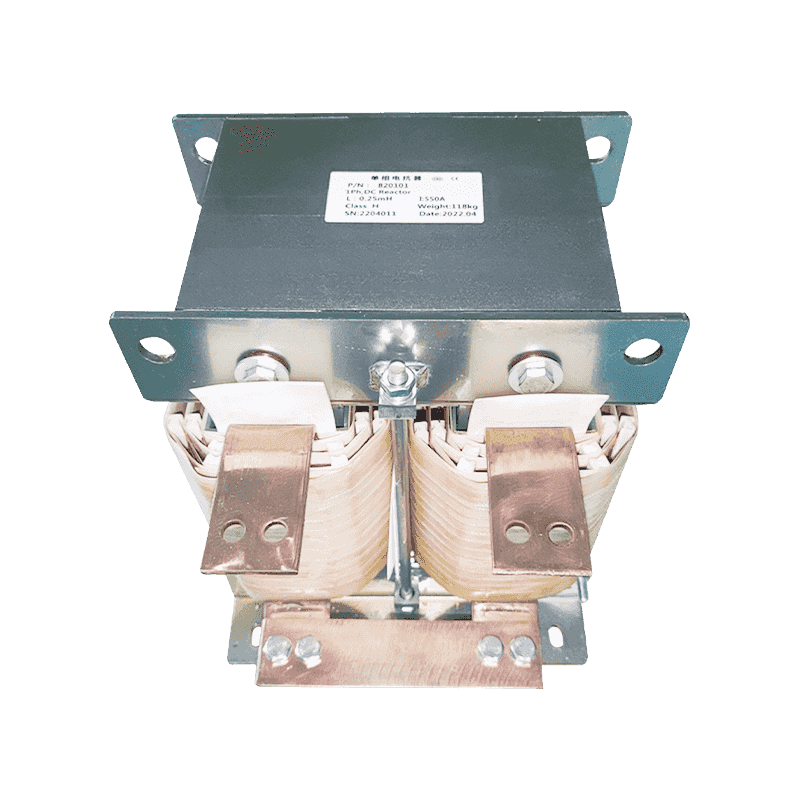
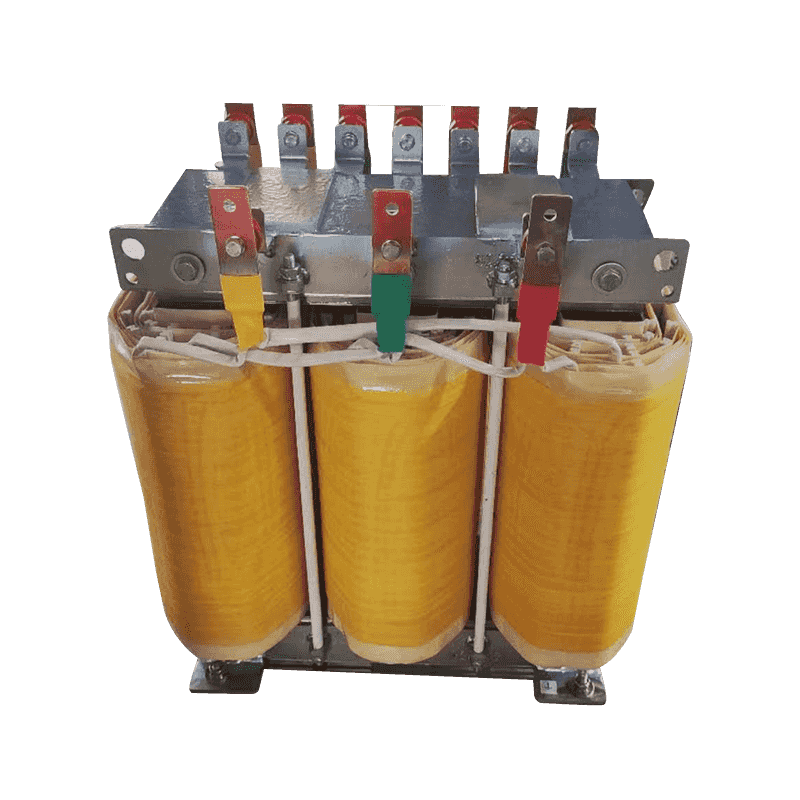
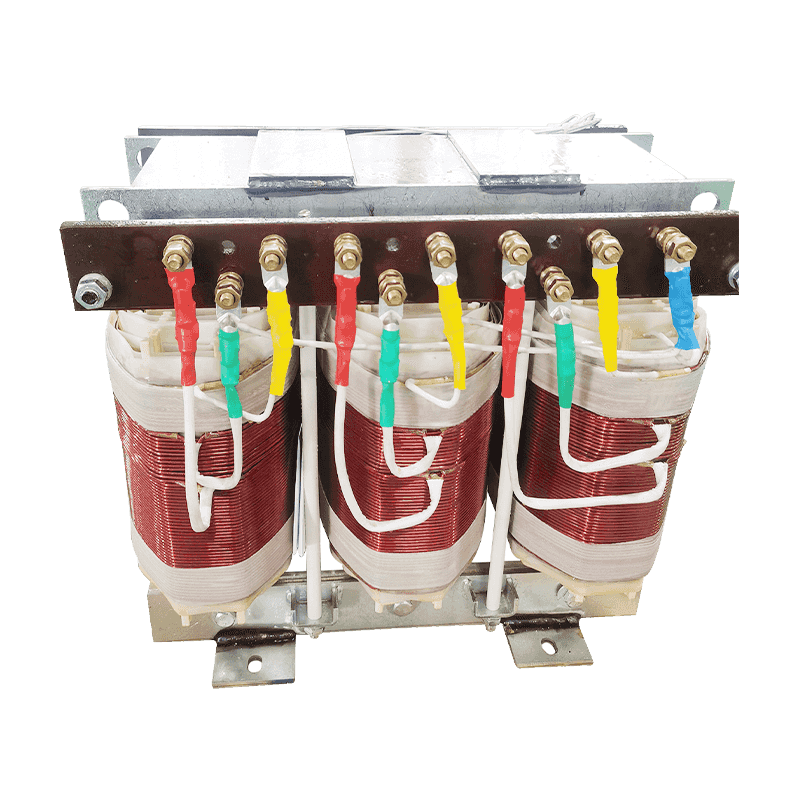
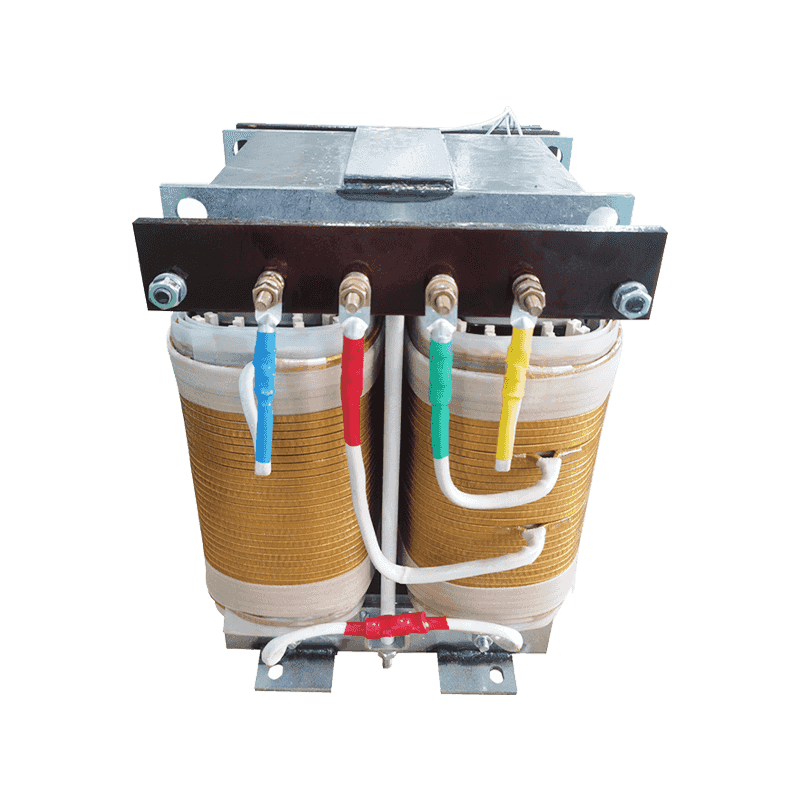
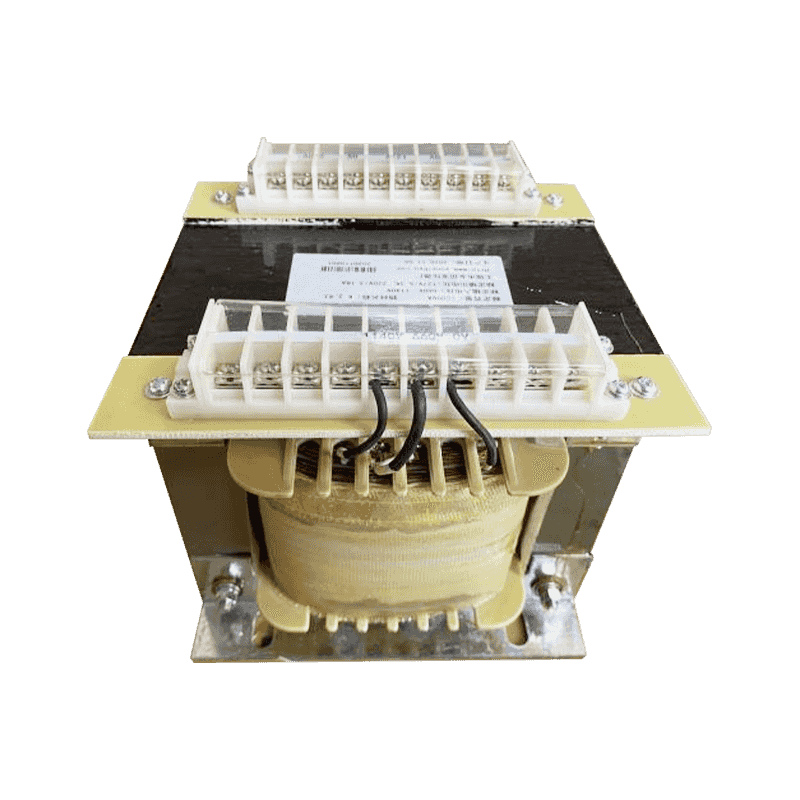
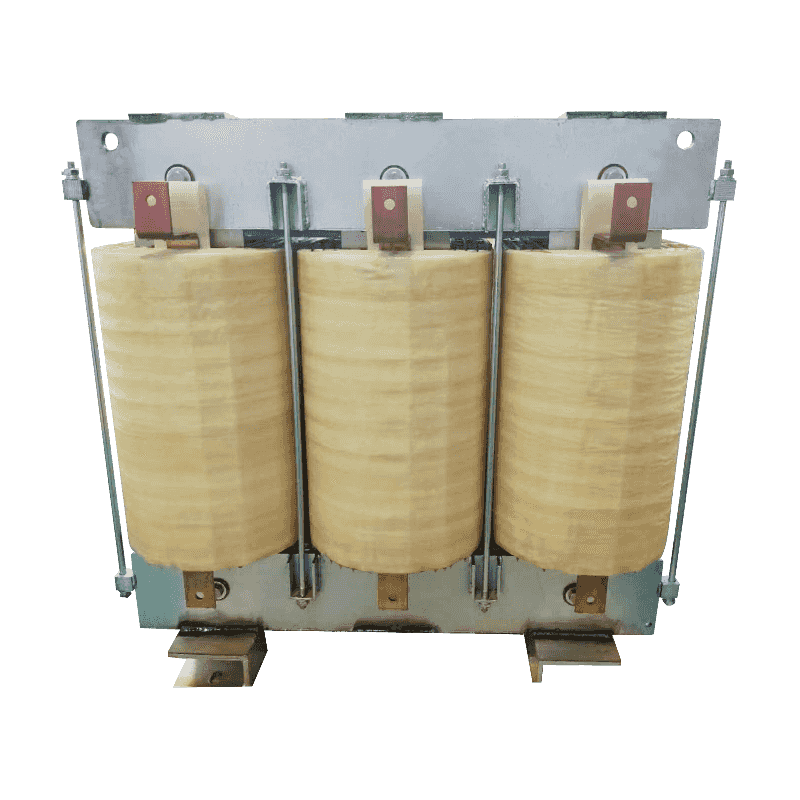
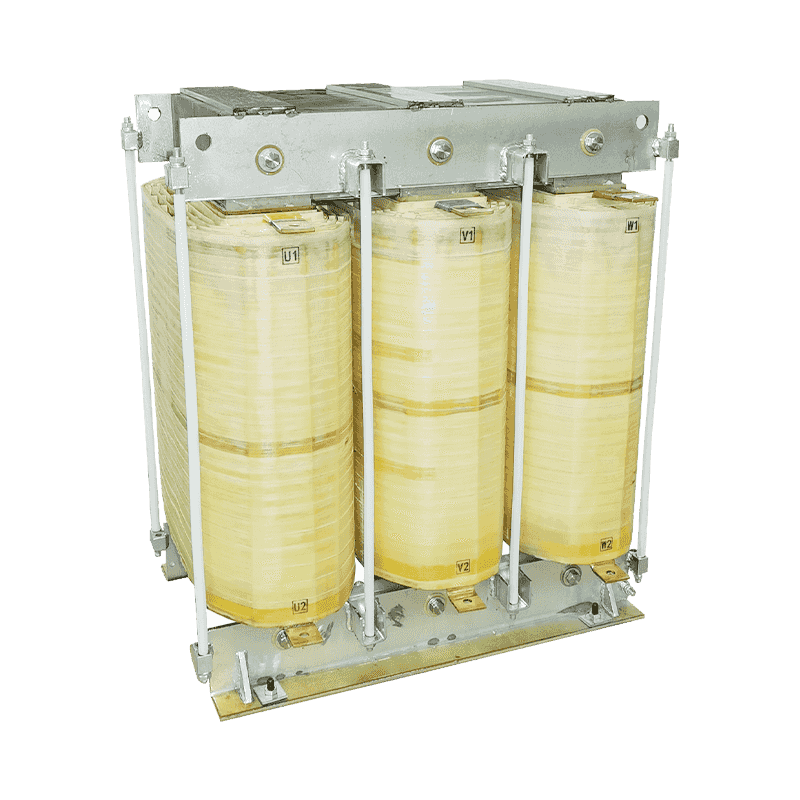
An autotransformer is a special transformer in which the output and input share a common set of coils. Step-up and step-down are realized with different taps. When the part of the taps less than the common coil voltage is reduced, and vice versa the part of the taps more than the common coil voltage is increased. The principle is the same as the ordinary transformer, except that its original coil is its secondary coil. The general transformer is the left side of a primary coil through electromagnetic induction so that the right side of the secondary coil produces voltage. But the autotransformer is affecting itself. An autotransformer is a transformer with only one winding, and when used as a step-down transformer, a portion of the turns are withdrawn from the winding to be used as the secondary winding. When used as a step-up transformer, the externally applied voltage is only applied to a part of the winding - the turns. The part of the winding that belongs to both the primary and secondary is usually called the common winding. The rest of the autotransformer is called the series winding. The same capacity autotransformer compared with ordinary transformers, not only small size, and high efficiency. The larger the transformer capacity, the higher the voltage. Therefore, with the development of power systems, the increase in voltage level, and the increase of transmission capacity, autotransformer is widely used due to their large capacity, low loss, and low cost.
| Capacity | 35 KVA |
| Rated Voltage | 208VAC |
| Primary Voltage | 208VAC |
| Secondary voltage | 380V |
| Frequency | 50/60Hz |
| Conductor material | Copper |
| Temperature rise | ≤ 65K |
| Noise | <70dB@1m |
| Isolation Class | H class |
| Cooling month | AN |

 Eng
Eng  Español
Español