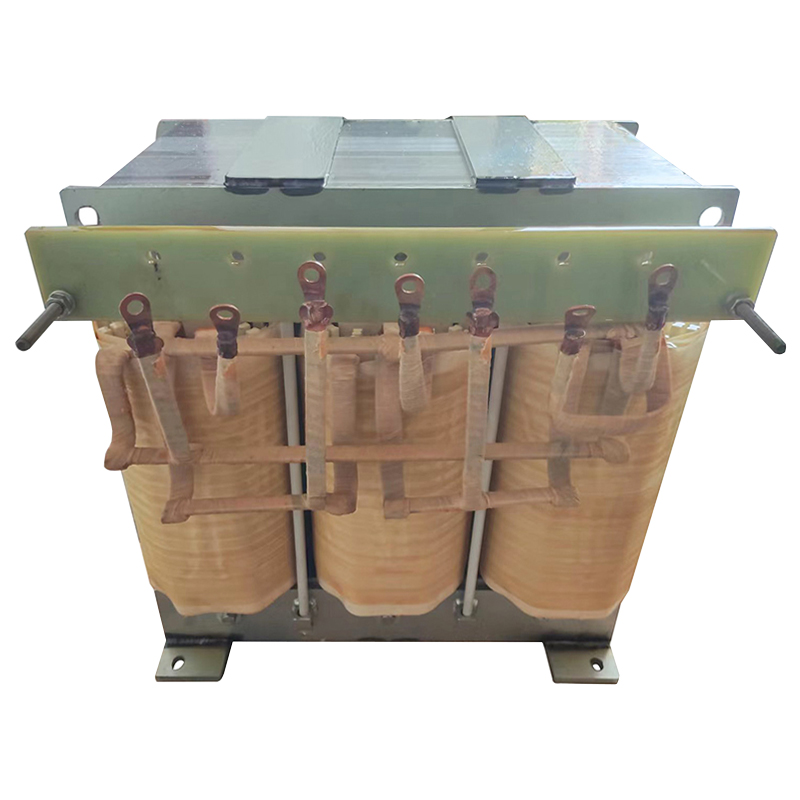
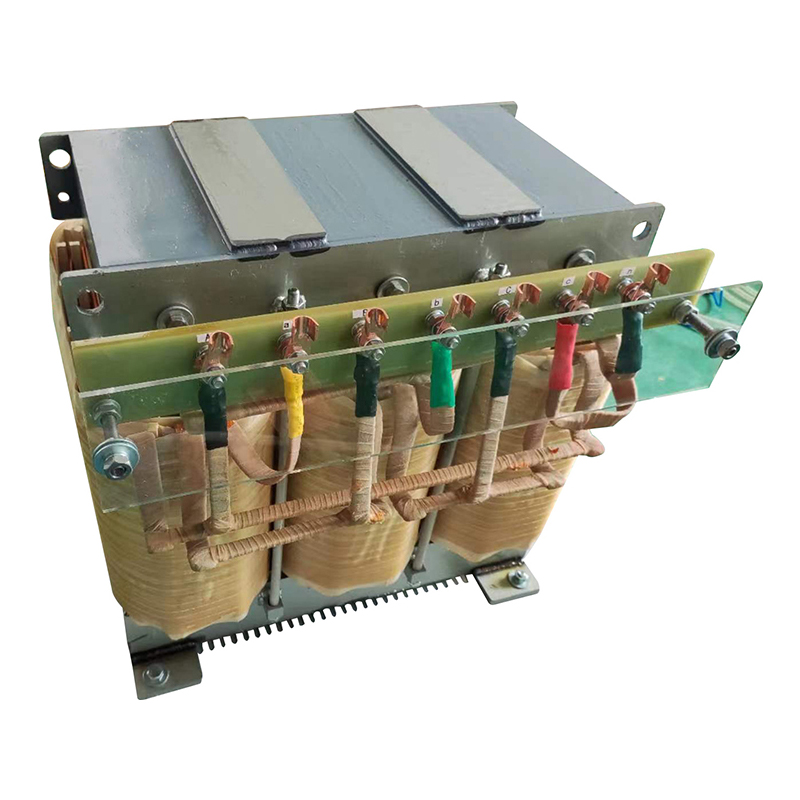
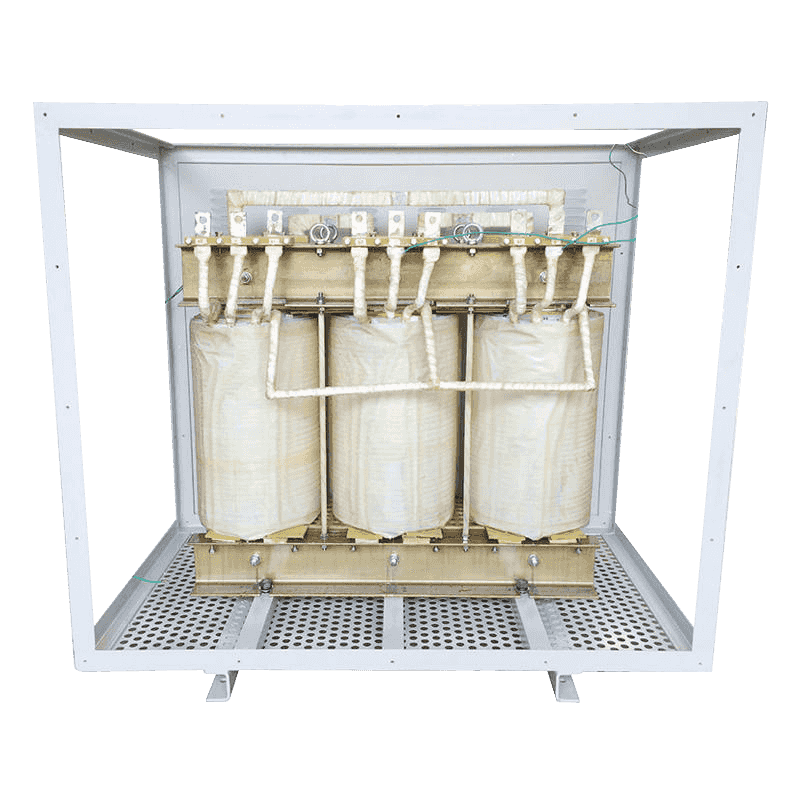
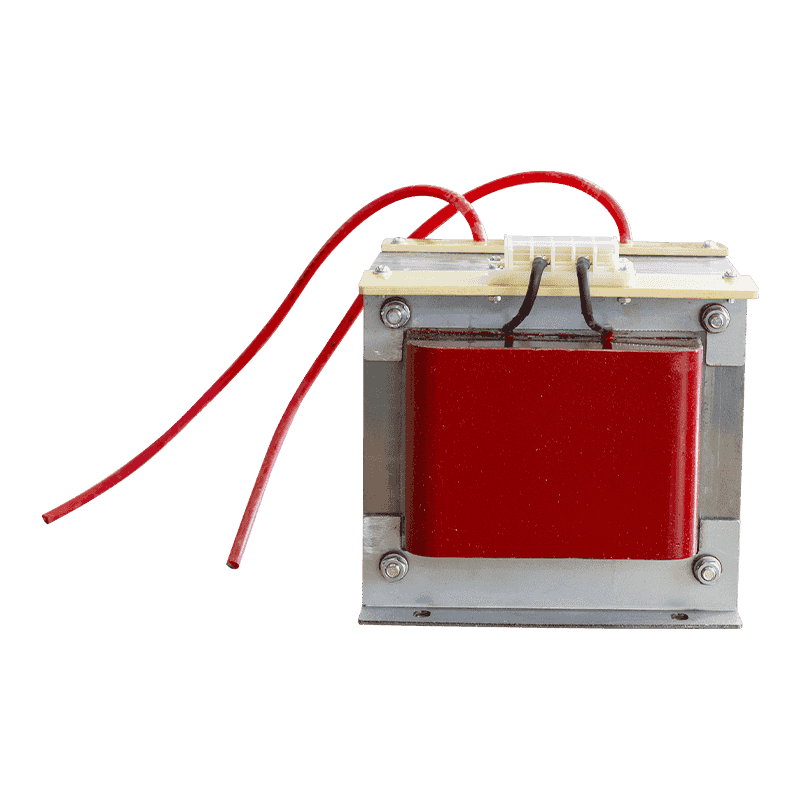
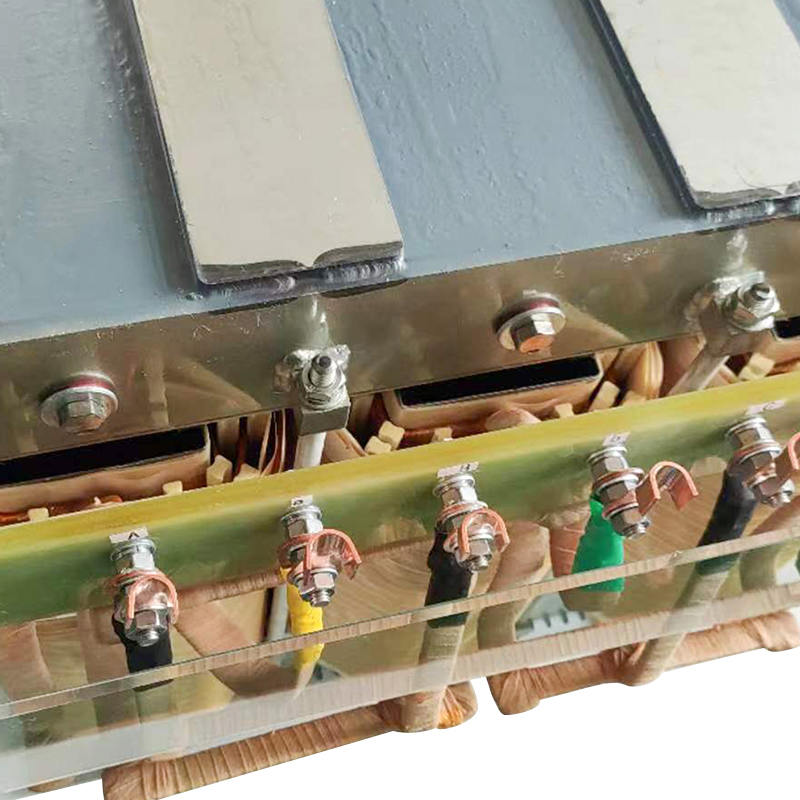
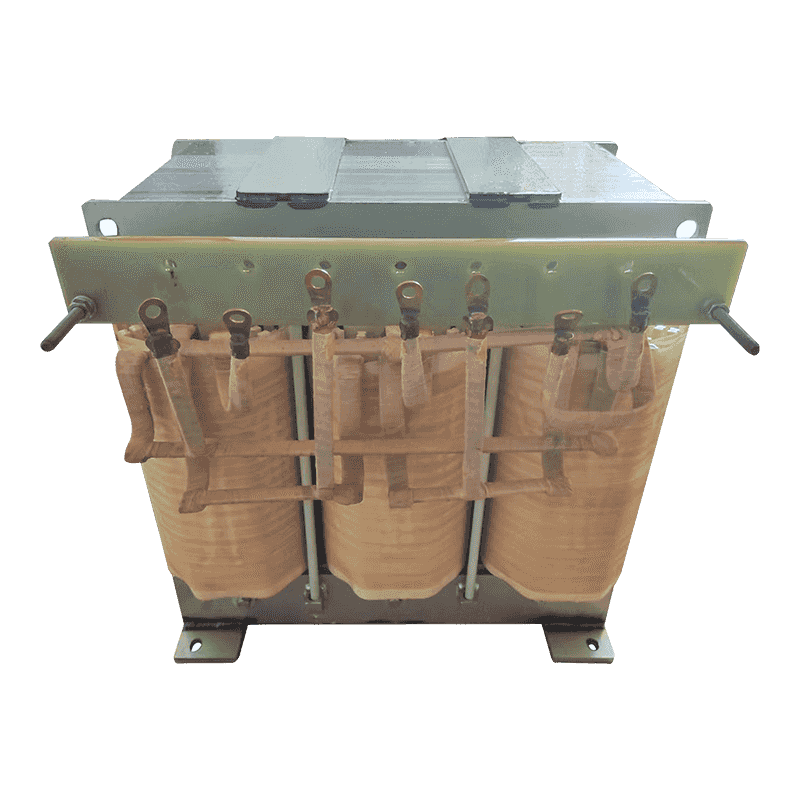
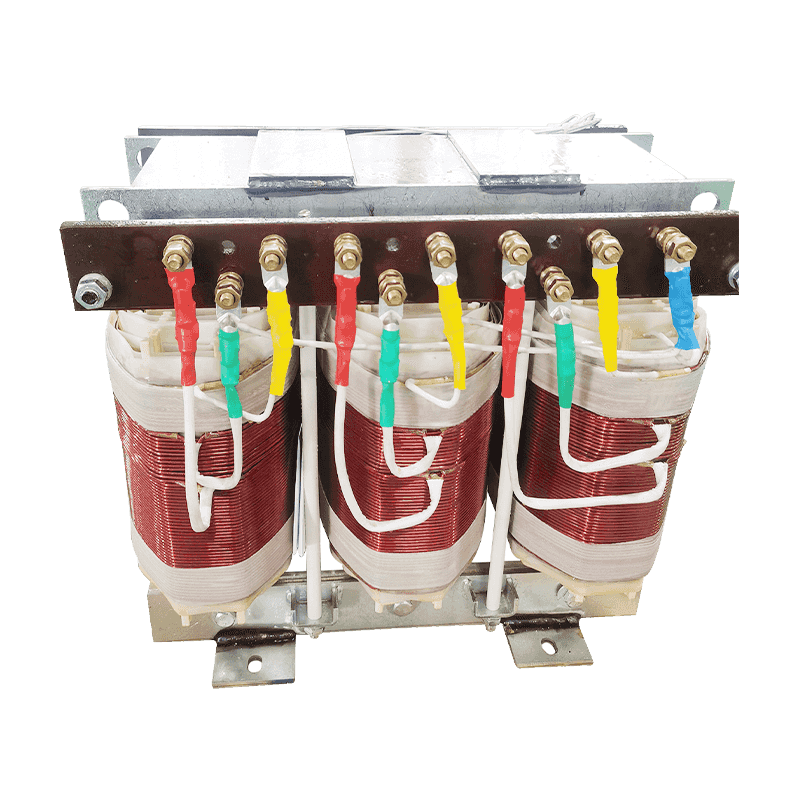
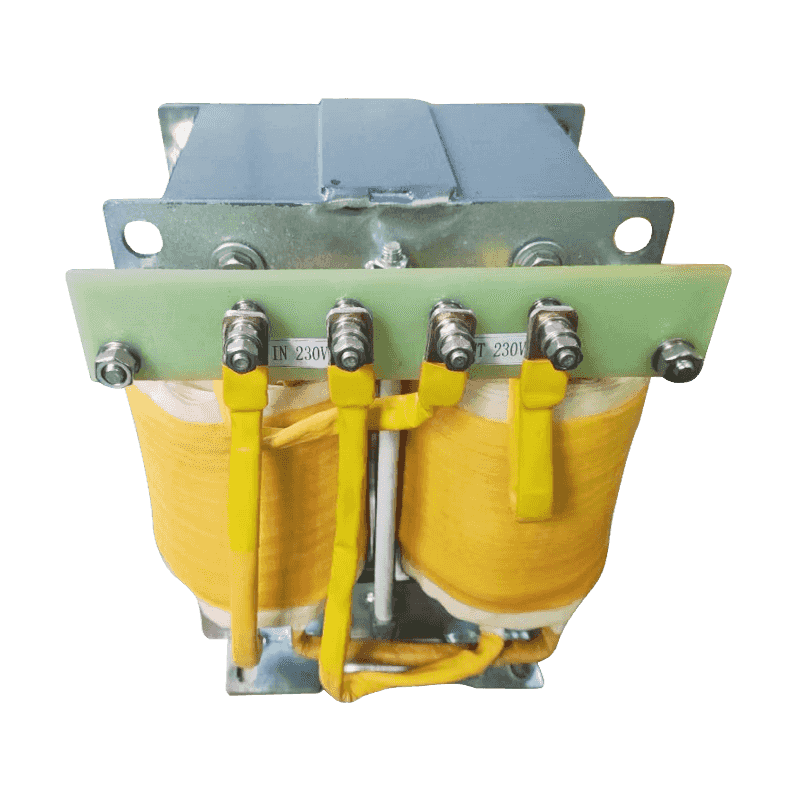
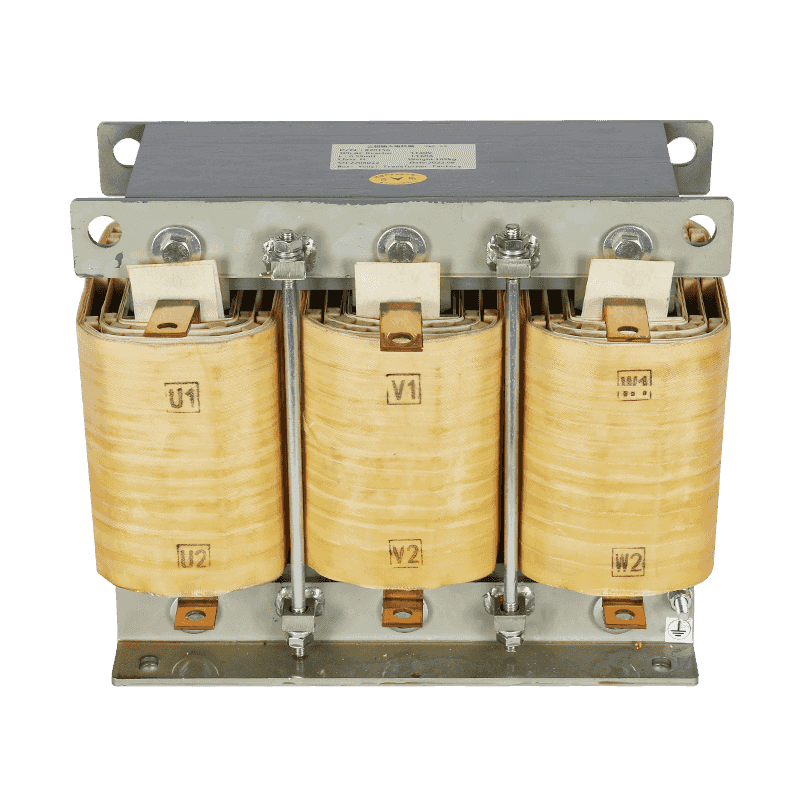
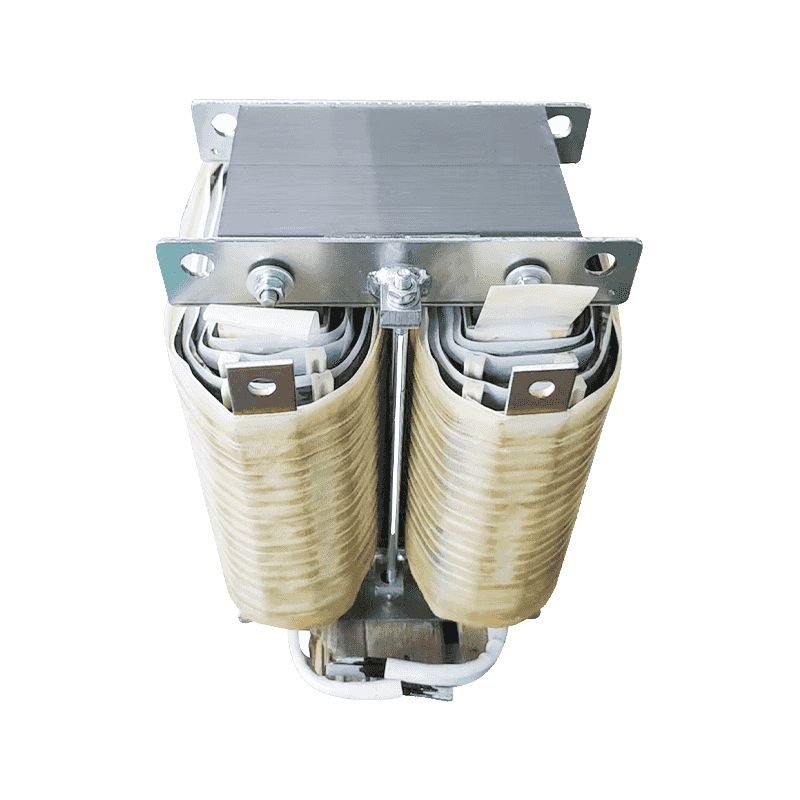
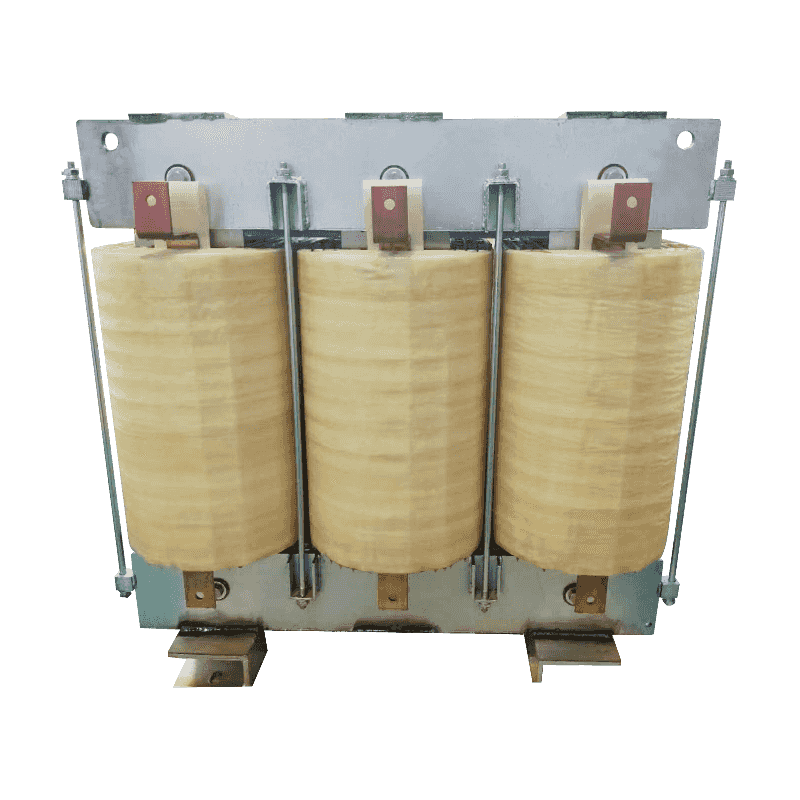
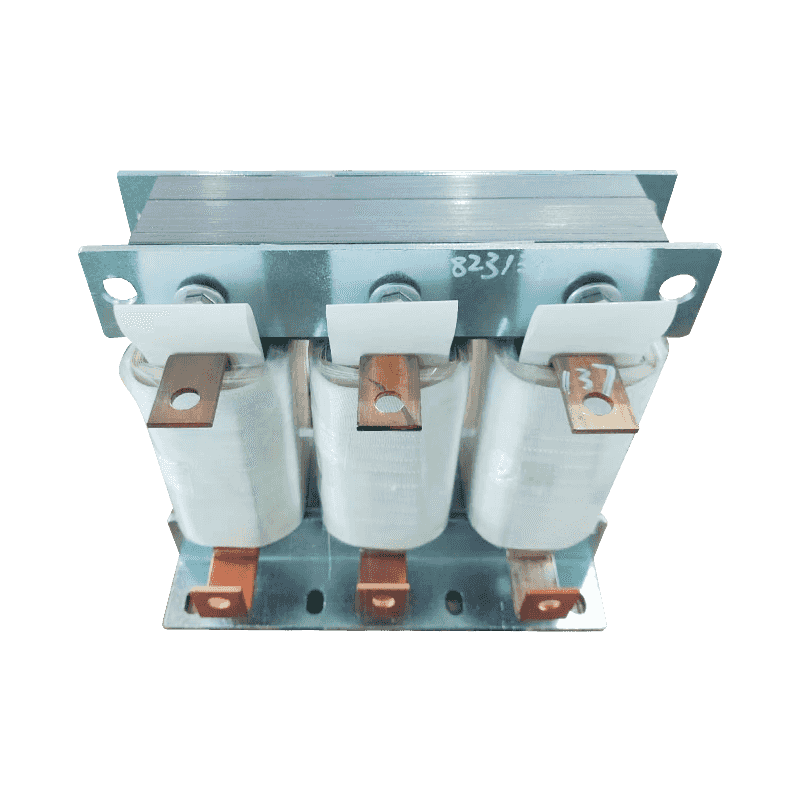
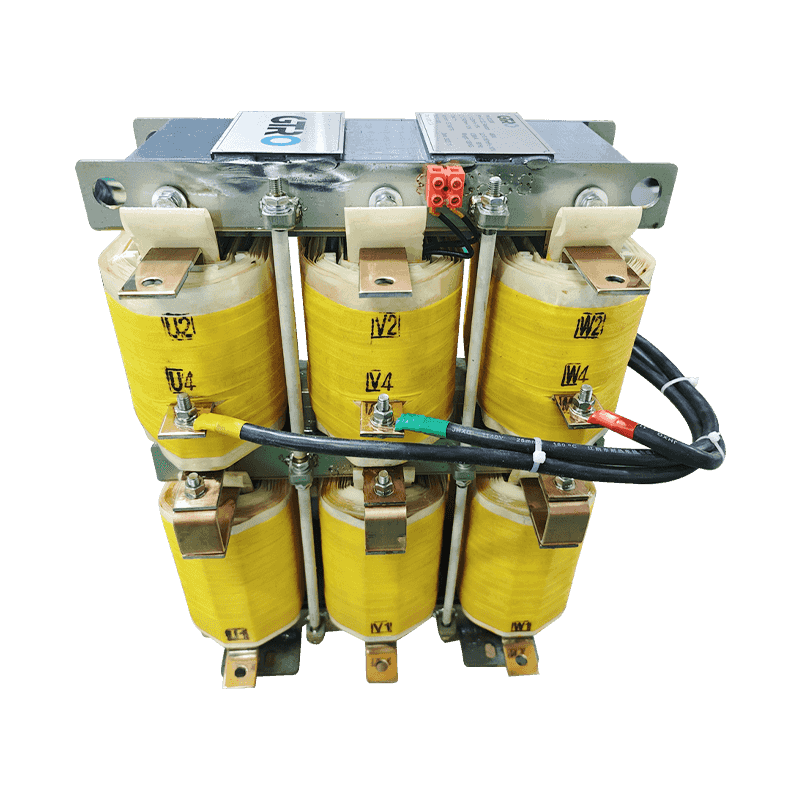
A three-phase transformer is a type of power transformer used to convert voltage from one three-phase circuit to another. They are widely used in power systems to regulate voltage, control current, and enable power transfer and distribution. A three-phase transformer usually consists of three separate coils, each of which is connected to each of the three-phase currents of the power supply. These coils can be magnetically coupled to each other on a shared core. One of the coils is connected to the input power supply and is called the main coil, while the other two coils are connected to the output load and are called the secondary coils. Different voltage conversions can be achieved by varying the turns ratio between the main and secondary coils.
Three-phase transformer with aluminum wire
1. Advantages
(1) Lower cost: Aluminum wire transformers of the same power are cheaper than copper wire transformers, so the economy is outstanding.
(2) Lightweight: Aluminum transformers are lighter in weight as compared to copper transformers and hence are easier to transport and install.
2. Disadvantages
(1) More serious heat: Aluminum transformers are easy to heat, so the service life is relatively short.
(2) Higher wire loss: Compared with copper transformers, aluminum transformers using aluminum as the winding material will to an increase in resistance when the current is transmitted, which will to energy loss.
|
Capacity |
30 KVA |
|
Rated Voltage |
230VAC |
|
Primary Voltage |
230VAC |
|
Secondary voltage |
480V |
|
Frequency |
50/60Hz |
|
conductor material |
AL |
|
temperature rise |
≤ 65K |
|
Noise |
<70dB@1m |
|
Isolation Class |
H class |
|
Cooling month |
AN |

 Eng
Eng  Español
Español